In the U.S., a COVID-19 diagnostic test is needed if:
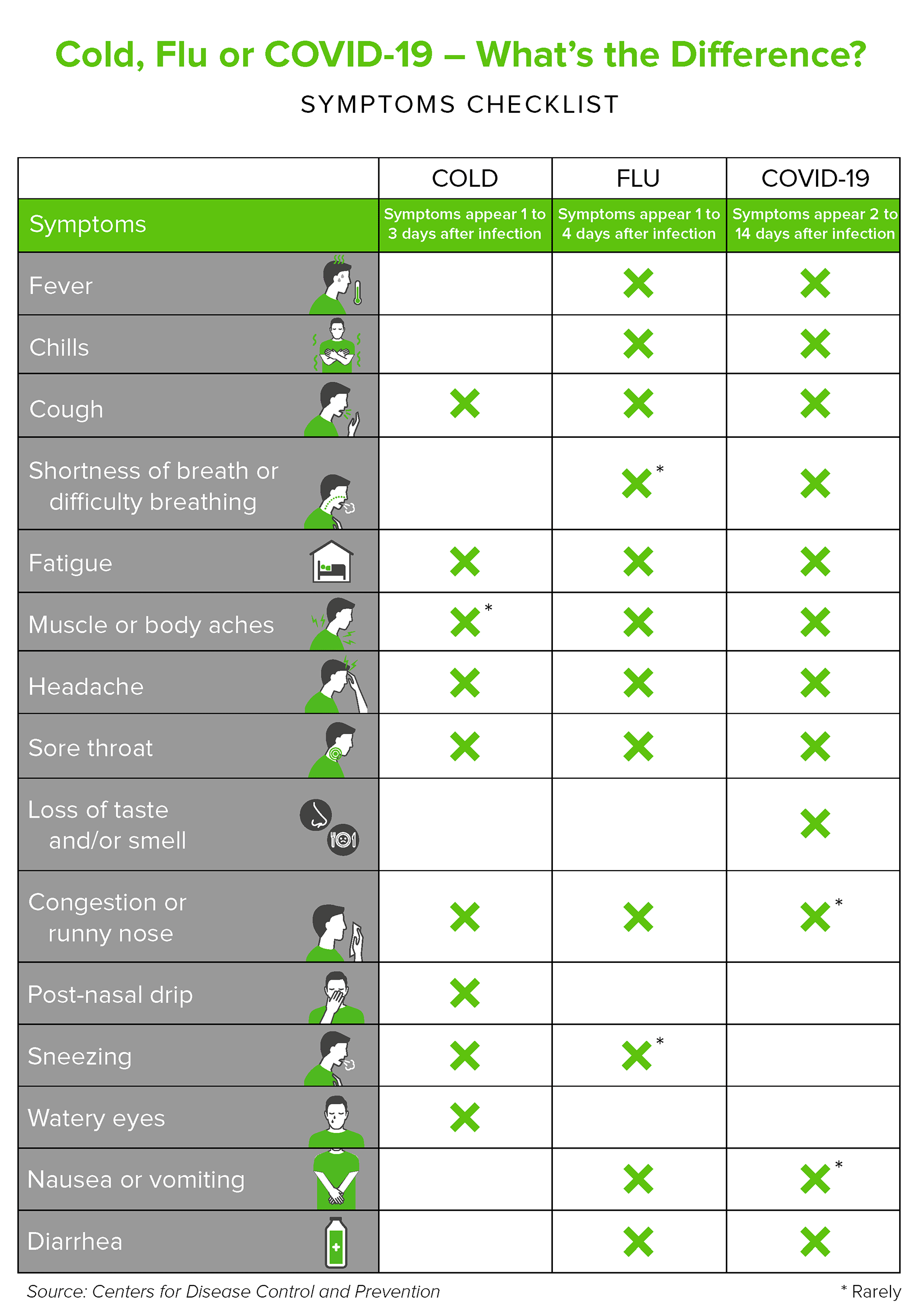
- You have COVID-19 symptoms, such as fever, cough, tiredness or shortness of breath, lost of taste and/or smell.
- You don’t have symptoms but you’ve had close contact with someone who tests positive for the COVID-19 virus or is suspected of having the virus. Close contact means you’ve been within 6 feet (2 meters) of a person who has COVID-19. But if you’ve tested positive for COVID-19 within the past three months, you don’t need to get tested. If you’ve been fully vaccinated and you’ve had close contact with someone who has the COVID-19 virus, get tested 3 to 5 days after you’ve had contact with them.
- You’ve participated in activities that increase your risk of COVID-19 and did not stay at least 6 feet away from others — examples include travel, large gatherings or crowded indoor settings.
- Your doctor or other health care professional or your public health department recommends a test.
Certain groups are considered high priority for diagnostic testing. These include people with COVID-19 signs and symptoms who:
- Work in a health care facility or as first responders
- Live or work in long-term care facilities, such as nursing homes, or other places where people are housed closely together, such as prisons or shelters
- Are being cared for in a hospital



